Introduction
The regulatory landscape for healthcare is undergoing a significant transformation as Real-World Evidence (RWE) becomes a key component in regulatory decision-making. In 2024, the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) published updated frameworks that integrate real-world data (RWD) into their evaluation process, increasing the credibility of RWE. Together, these initiatives highlight a unified commitment to leverage RWE which gives way to the emergence of more innovative business use cases across the healthcare industry focusing on the quality of evidence for better outcomes.

The Evolution of Real-World Evidence: Early Applications
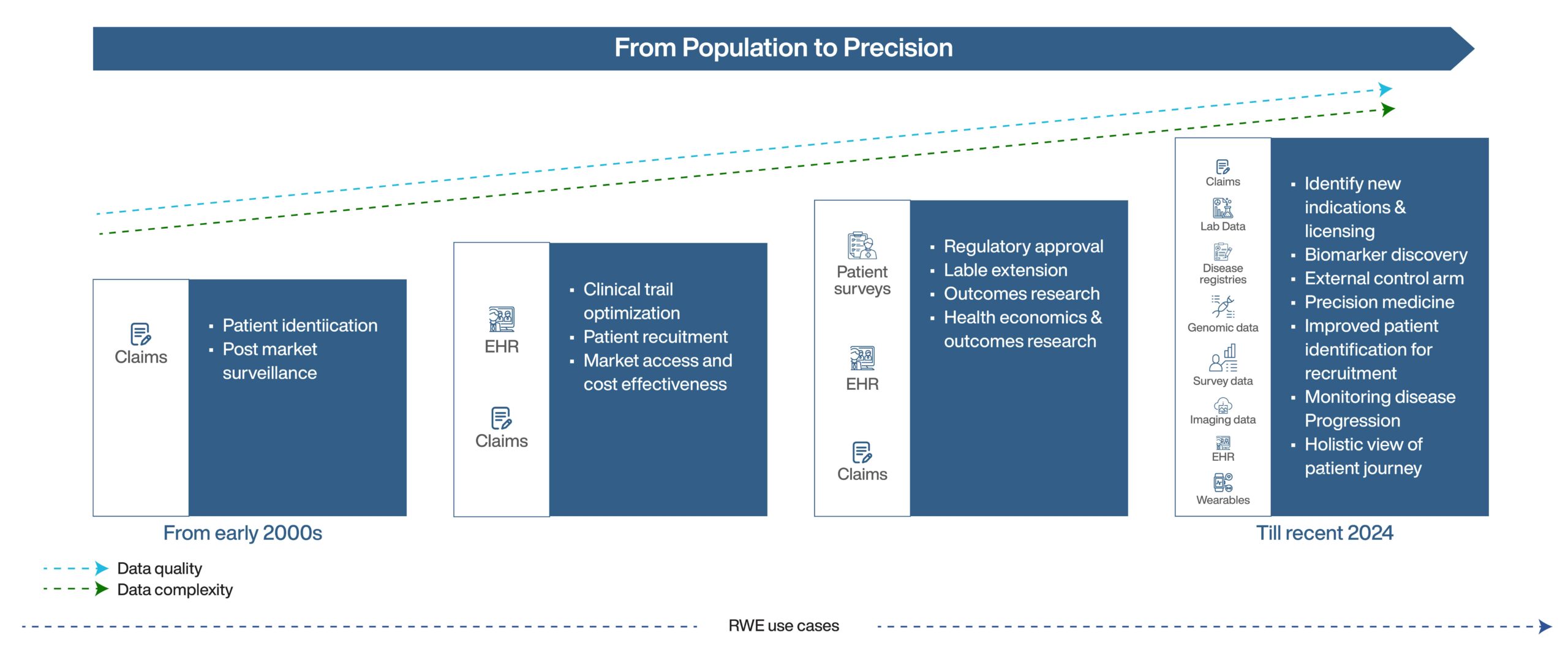
Close to a decade ago, real-world evidence was still in its emerging point, with data drawn mostly from electronic health records, claims databases, and patient registries. However, key industries began to utilize RWE to address emerging challenges and opportunities in real-world healthcare. Among these industries, the first one that readily adopted RWE was the pharmaceutical industry. The initial use case was to support and complement the evidence generated by traditional randomized controlled trials (RCT’s). Along with this, RWE also provided an enhanced understanding of the disease, improving safety and lowering product cost. Similarly, the MedTech organizations also started utilizing RWE to support regulatory submissions and post-market surveillance to capture the effectiveness of devices. Other industries tapping into the RWE space were the healthcare providers and insurance industry which leveraged RWE for better understanding and outcomes.
When reviewing the earliest use cases of RWE in the healthcare space, the first was post-market surveillance, specifically for drugs and medical devices. The next use case would be patient identification to identify subgroups deriving the most benefit from a specific treatment. As healthcare costs continued to rise RWE also became an effective tool in health economics and outcomes research supporting better decision-making in effectiveness assessments.
Over the years, RWE has moved its position from a niche concept to a critical tool in healthcare. The focus has evolved from focusing on sheer volume of data to delivering precise and high-quality evidence. By integrating diverse data types, RWE provides a comprehensive understanding of the patient journey and treatment. With these shifts, the recent use cases of RWE include biomarker identification, external control arm, label expansion, risk, and drug repurposing to name a few.
Innovation in Business Use Cases: Key Factors Behind the Evolution
A. The vast wealth of RWE data which was once fragmented and limited in scope has undergone a remarkable transformation with the shift towards precision enabling quality data. RWE’s initial sources were limited, mainly claims, EHRs, patient registries, and surveys. Today the scope of RWE has expanded further with the inclusion of advanced data sources like genomic data and imaging data( from radiology and pathology), which are enriched with granular clinical details more representative of the real-time clinical situation. Due to increased access to these datasets, integrating them enables the development of more innovative use cases for RWE.
B. The advent of AI has also been a driving factor for innovation in business use cases. By leveraging ML and NLP models, AI enables easier and faster processing of large, complex, and multi-modal datasets. As we move into the future, these multi-modal datasets can be utilized for training and validation of AI algorithms for more accurate diagnosis, disease tracking, etc.
C. Traditionally RWE provided insights on population level, revealing broad trends and treatment outcomes. But now as the emphasis shifts toward precision medicine, by integrating data from different sources like EHRs, patient registries, and genomic and imaging data, stakeholders can pinpoint subpopulations enabling a more targeted treatment approach.
D. Initially, use cases of RWE were focusing narrowingly on comparing the cost of interventions to health outcomes. This approach has now transitioned to address long-term safety and effectiveness, patient-reported outcomes, societal impact, health equity, and value-based pricing. By integrating insights like the quality of life, and healthcare burden RWE is now driving a deeper understanding of healthcare value paving the way for patient-centred solutions.
Evolution of RWE Business Use Cases
- Clinical Trial Optimization and the transition towards external control arms
Traditionally role of RWE in clinical trials was to support safety and efficacy evaluations, identify patients for recruitment, and evaluate real world endpoints. However as the healthcare landscape evolved, certain challenges like patient recruitment and the aim to shorten drug approval time have fuelled a shift where the focus is on leveraging RWE to create external control arms for clinical trials. Notably, this also reflects a broader shift where emphasis is now on prioritizing high-quality evidence generation. External control arm as a use case can lower the cost associated with clinical trials while accelerating the evaluation process.
- Shift from a single research question to multiple research question solutions
Initially, with limited knowledge of RWE, its use was constrained to one-time single-use cases for eg, tracking adverse events for a specific subset of cancer. But as the understanding of RWE increased it laid the foundation for considering solutions that tackle multiple use cases at a time. The availability of advanced data platforms/networks has enabled the integration of multiple data types from global data sources (e.g. EHRs, claims data, real world imaging data, patient-reported outcomes, and lab results). Along with the availability it is now imperative to provide integrated data of immense quality for better outcomes. Integration, data enrichment, and anonymization capabilities have provided avenues for building efficient and cost-effective solutions that cater to multiple use cases at a time.
- RWE for rare diseases: Then vs now
In the past RCTs for rare diseases faced barriers related to a limited pool of patients, requiring long-term follow-up and the determination of appropriate clinical end points. Given these circumstances, RWE found its place in supporting market access and reimbursement decisions for treatment. However, now linking fragmented patient-level datasets has become significantly easier which has unlocked a new application of RWE: the use of historical controls. HCs can be derived from a variety of data sources, including patient registries, and medical charts which when analyzed can establish robust historical controls reducing the number of patient recruitment and accelerating drug approval.