In today’s complex healthcare landscape, ensuring patient safety and delivering high-quality care have become paramount. Medical errors are alarmingly prevalent, with estimates suggesting that over 200,000 patients die annually in the U.S. due to preventable medical errors . These errors not only have a profound human cost but also impose significant financial burdens, with adverse events costing the healthcare system billions each year.
As healthcare systems increasingly integrate advanced technologies like electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine, and AI-driven diagnostics, the complexity of care delivery grows. This evolution necessitates robust Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) mechanisms to ensure that healthcare services are safe, effective, and compliant with regulatory standards.
The Rise of Intelligent Telemedicine Assistants
The global telemedicine market is projected to grow from USD 286.22 billion in 2025 to USD 458.06 billion by 2033 (CAGR 7.2%), driven by digital health transformation and demand for scalable care models. A significant part of this growth is fueled by the increasing integration of AI-powered assistants into telehealth platforms. For instance, the AI in telemedicine market is expected to reach USD 156.7 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 26.1%.
In 2024, the CDC reported that 25% of all U.S. healthcare visits occurred via telehealth – up from just 7% in 2018. Now, platforms are evolving from static video chats to intelligent, assistant-led workflows that guide patients and support clinicians before, during, and after consultations.
Key Drivers Behind Telemedicine Assistant Adoption
- AI and Automation: Telemedicine assistants leverage natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and rule-based logic to triage symptoms, interpret patient queries, and route them to appropriate care pathways.
- Chronic Disease Demands: Managing hypertension, diabetes, and COPD requires regular touchpoints - AI assistants automate monitoring, reminders, and alerts to improve compliance.
- Rural and Underserved Access: Virtual assistants reduce dependency on physical infrastructure, making care accessible in remote or overburdened urban areas.
- Cost and Efficiency Pressures: Automating routine tasks such as intake forms, medication adherence checks, and appointment reminders reduces staffing burdens and improves throughput.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike human operators, telemedicine assistants provide round-the-clock support, ensuring patient engagement isn’t limited to clinic hours.

How Telemedicine Assistants Work: A Typical Workflow
Smart Intake and Symptom Triage
Patients initiate care through an app or web portal. A conversational assistant collects symptoms, history, and risk factors using guided dialogue or voice input.
AI-Powered Triage
Based on symptom data, the assistant provides preliminary risk assessment and determines urgency – routing patients to self-care, a general practitioner, or a specialist as needed.
Automated Appointment Scheduling
Once triaged, the assistant schedules an appropriate consultation – factoring in doctor availability, time zones, and preferences – and sends reminders via SMS or app notifications.
Virtual Consultation Preparation
Before the appointment, the assistant sends checklists, intake summaries, and guides to patients, preparing both them and the clinician for an efficient consultation.
In-Session Support
During the telehealth visit, assistants can take notes, pull up relevant history, display patient-reported symptoms, or translate medical terminology for the patient.
Post-Visit Follow-Up & Adherence Support
After the consult, assistants handle follow-up scheduling, medication reminders, patient education, and asynchronous queries – helping patients stay on track.
Ongoing Monitoring
Integrated with wearable or remote monitoring devices, assistants track vitals like glucose levels or blood pressure, triggering alerts or virtual check-ins when anomalies are detected.
Example Workflow: AI-Powered Telemedicine Assistant
In a modern telemedicine platform, intelligent assistants streamline patient interactions through a seamless, multi-step process:
System Initialization
The platform loads necessary environment configurations and initializes integrations with Twilio for communication services and Groq for AI-driven responses.
User Interface Engagement
Patients access the platform via a user-friendly interface, selecting their preferred language and choosing from services such as Health Advice, Appointment Scheduling, or Video Consultation.
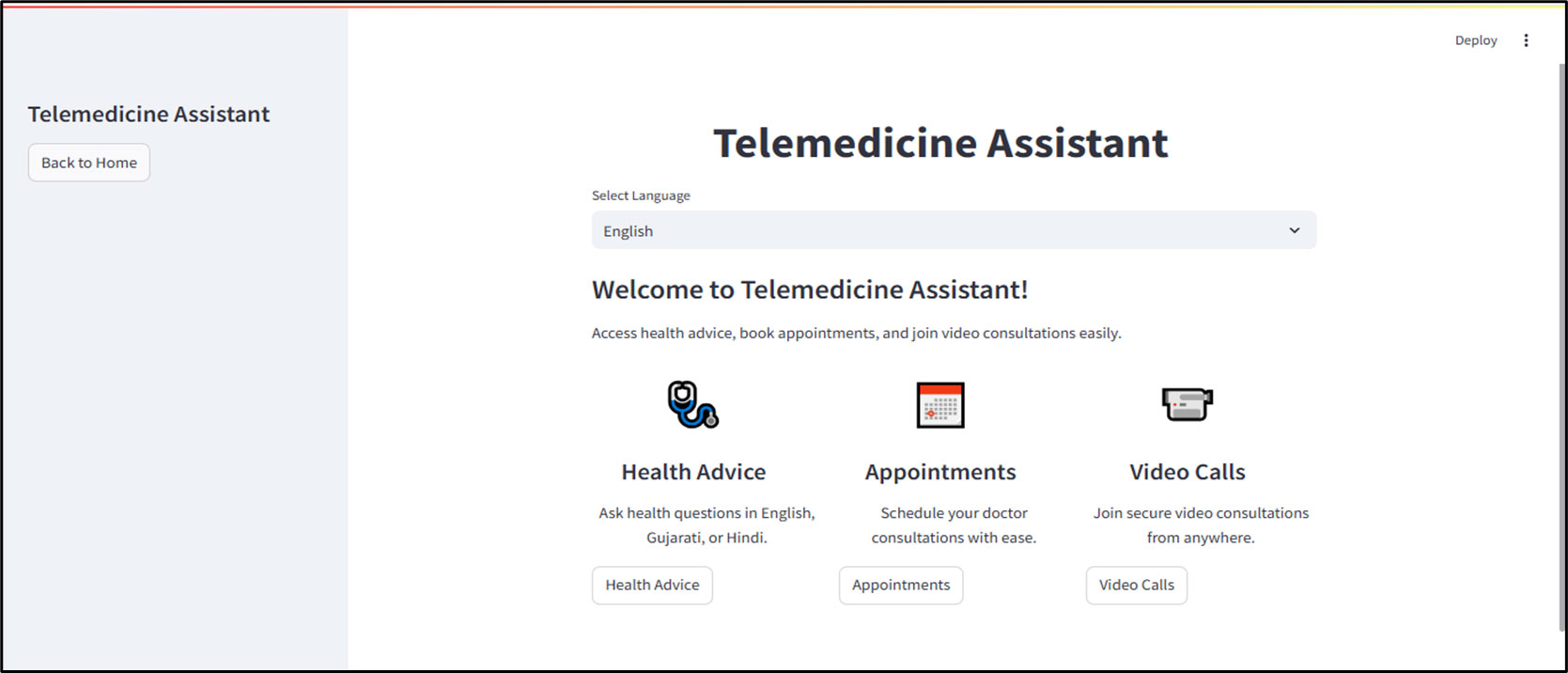
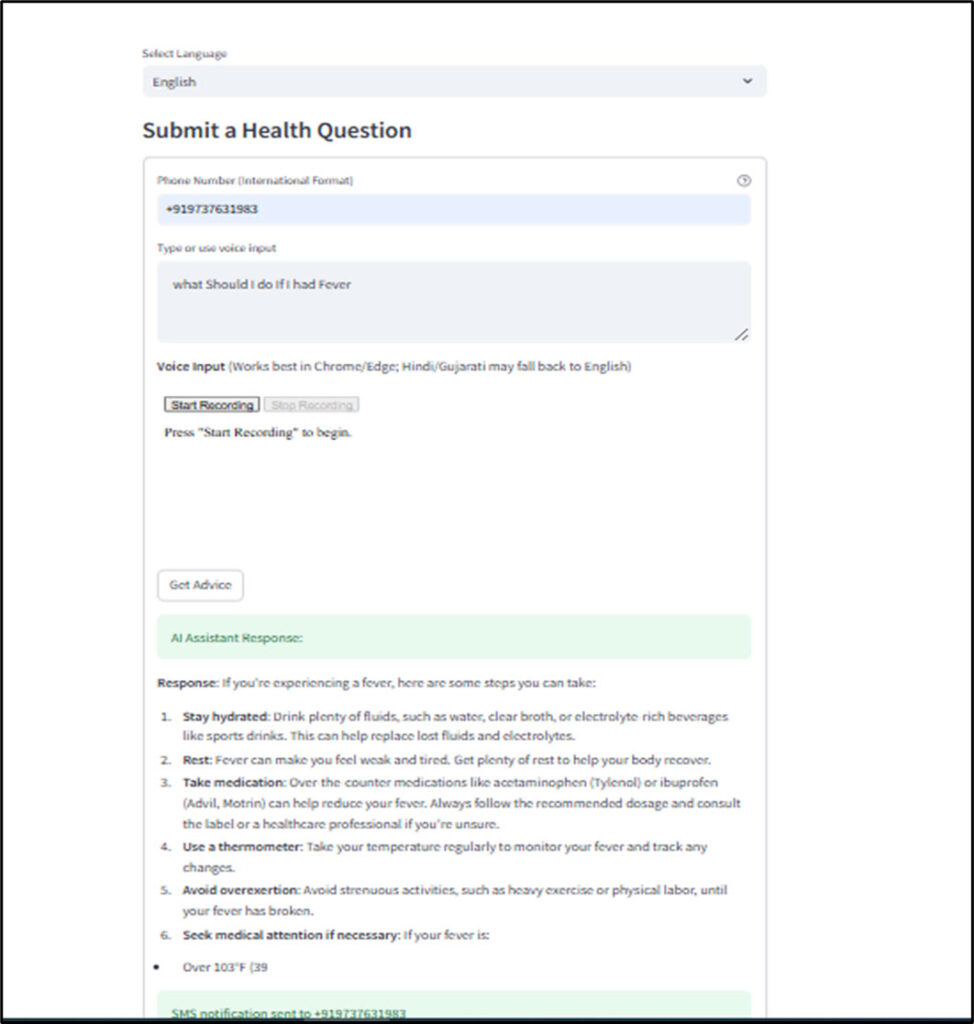
Health Advice Interaction
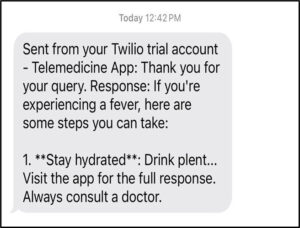
When seeking health advice, patients input their queries through text or voice. The AI assistant processes these inputs, generating informative responses that are displayed on-screen and sent via SMS for convenience.
Appointment Scheduling
For scheduling appointments, the assistant guides patients through selecting suitable dates and times. Once confirmed, the system sends SMS reminders to ensure patients are informed of their upcoming consultations.
Real-Time Video Consultation
Patients opting for video consultations are connected to healthcare providers through secure video links. The assistant facilitates the session by providing necessary information and support throughout the consultation.
Dynamic Session Management
The platform employs Streamlit to manage dynamic session states, ensuring smooth transitions between different stages of interaction. Robust error handling mechanisms are in place to manage any API-related issues, maintaining a reliable user experience.
Post-Consultation Support
After consultations, the assistant continues to support patients by sending follow-up messages, managing prescription reminders, and providing additional health resources as needed.
Use Cases for Telemedicine Assistants
- Chronic Health Management
- Daily Check-Ins: Automated prompts for symptom tracking or lifestyle habits.
- Remote Monitoring: Alerts clinicians to worsening conditions using device data.
- Medication Adherence: Reminders and visual aids help improve compliance.
- Triage and First-Line Support
- Symptom Assessment: Natural-language chatbots guide patients through triage trees.
- Health Advice: Instantly provides validated health education for mild symptoms.
- Emergency Routing: Identifies red flags and escalates to urgent care or emergency services.
- Patient Engagement and Education
- Personalized Education: Post-consultation material delivered in multiple languages and formats.
- Lifestyle Coaching: Guided support on diet, sleep, and mental health through continuous engagement.
- Clinical Trial Enablement
- Participant Support: Assistants guide trial subjects through informed consent, protocol adherence, and digital diaries.
- Data Collection: Automates survey distribution and collects patient-reported outcomes.
- Visual & Store-and-Forward Assistance
- Image Sharing: Patients securely upload photos (e.g., skin lesions, wounds) for asynchronous review.
- Smart Documentation: Assistants format and summarize submitted materials for clinician review.
Benefits of Telemedicine Assistants in Healthcare
Scalable Care Delivery
Handles thousands of patient interactions simultaneously—ideal for large health systems or clinical trial networks.
Reduced Clinician Burden
Automates repetitive tasks, freeing up time for clinicians to focus on complex care decisions.
Continuous, Proactive Care
Enables longitudinal engagement rather than episodic touchpoints, improving health outcomes.
Improved Patient Satisfaction
Patients feel supported, informed, and connected—leading to better adherence and retention.
Lower Operational Costs
Reduces staffing, administrative, and infrastructure overhead—while increasing care access.
Multilingual, Culturally Tailored Support
Assistants can be customized for language, literacy, and cultural sensitivity – supporting diverse populations.
The future of telehealth isn’t just virtual – it’s intelligent. Telemedicine assistants are redefining patient engagement, clinical efficiency, and chronic care management. As healthcare systems strive to deliver high-quality care at scale, these assistants act as critical front-line workers – always available, ever-consistent, and deeply capable. With continued advances in AI, speech recognition, and personalized care algorithms, telemedicine assistants will become an indispensable part of the modern healthcare experience.
Healthcare is evolving faster than ever — and those who adapt are the ones who will lead the change.
Stay ahead of the curve with our in-depth insights, expert perspectives, and a strategic lens on what’s next for the industry.




